Disk Instructions
How to Get Our Programs Up and Running
Each article in this issue with a disk icon on its first page (or next to its title on the Table of Contents) has a companion file on your START disk. These files are archive files--they've been compressed with the Archive Utilities Set, or ARC, a public domain program available for many personal computers. We use the ARC utility to squeeze the many files that may go with a particular article into one compressed file, which may be only 40% of the total size of the original files.
In addition to the archive files, you'll find the program ARCX.TTP, which stands for ARChive eXtract, on your START disk. You'll use this program to decompress, or extract, the disk files we've shrunk down with ARC.
Getting Started
To use the files and programs on your START disk, please follow these simple instructions. You'll need two blank, formatted single- or double-sided disks to properly extract the files.
Your START disk is not copy-protected and you should make a copy of it immediately to the first blank disk. Make sure the write-protect window is open on the START disk at all times to insure that you don't accidentally erase the disk.
Note: If you are unsure how to format a disk, copy a disk or copy individual files, please refer to your original Atari ST or Mega manual and study these procedures carefully before going on.
After you've copied your original START disk, store it in a safe place and label the copy disk "START Backup."
Now, put your START Backup disk in Drive A of your computer and double-click on the Drive A icon to see the disk's contents.
Un-ARCing the Files
To use START's compressed disk files, please follow these steps:
1. Copy the ARCed file you wish to use and the program ARCX.TTP from your START Backup disk onto your second blank formatted disk. When you're finished, label it UN-ARC disk.

2. Now you'll extract the compressed files from the ARC file you just copied. Insert your UN-ARC disk into Drive A and press the Escape key on your ST to see the disk directory. Double-click on ARCX.TTP. The following dialog box will appear:
3. Type in the name of the ARC file you just copied over to your UN-ARC disk as shown in the example below .and press Return. You do not have to type in the extender.ARC.
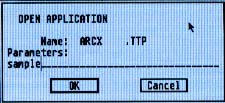
(Note: If ARCX.TTP can't find a file, it may be because you have misspelled the name of the ARC file. You must type the filename exactly as it appears in the directory.)
4. As the program runs, it will display the names of the individual files as it extracts them, similar to the example below
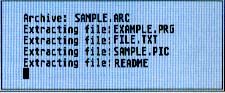
When ARC has successfully extracted all the files, it will return to the Desktop and you will see the original files within the directory window, along with the archive file and the ARCX.TTP program. You may now use any of the START files as you wish; just follow the instructions in the appropriate article in this issue.
To use any other archive files on your START disk, simply repeat the above procedures.
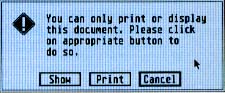
In addition to the runnable programs, some ARC files may also contain source code listings or an ASCII text file (called BREAKDWN.TXT, for example) which describes the program's structure. You can examine this file from the ST Desktop by double-clicking on its icon and then clicking on Show (to see it on the monitor) or Print (to print it out) as shown in the example below.
|